由浙江大学中国农村发展研究院、公共管理学院易福金教授与博士研究生刘辉琳、权泉合作完成的论文“Impacts of climate change on agricultural chemical inputs: Evidence from pesticide usage in China”在国际农经领域权威期刊Agricultural Economics在线发表。截至今年8月,卡特师生已在本刊的农业资源与环境、农业生产、土地管理、食品消费等多个领域形成5篇高水平论文的井喷式发表,进一步丰富了学科建设的内涵,保持了研究方向的均衡发展。

英文摘要
Pesticides are commonly used for pest control to improve crop yield and quality. Global warming has been suggested to influence pest pressure and optimal pesticide utilization. This study systemically assesses the impacts of rising temperatures on pesticide usage based on novel panel data from China during 1998−2016. Estimation results show a nonlinear relationship between pesticide usage and temperature. This effect is notably more pronounced in southern China compared to the north, especially under extremely hot weather conditions. The overall influence of temperature on pesticide usage is further broken down into three components: pesticide usage intensity, crop mix, and total planted area. Owing to the limited potential for expanding cultivation in China, the intensity effect dominates the impacts of temperature on pesticide usage. The findings indicate that the increase in temperature over the past two decades has led to a moderate reduction in pesticide usage in China.
中文概要
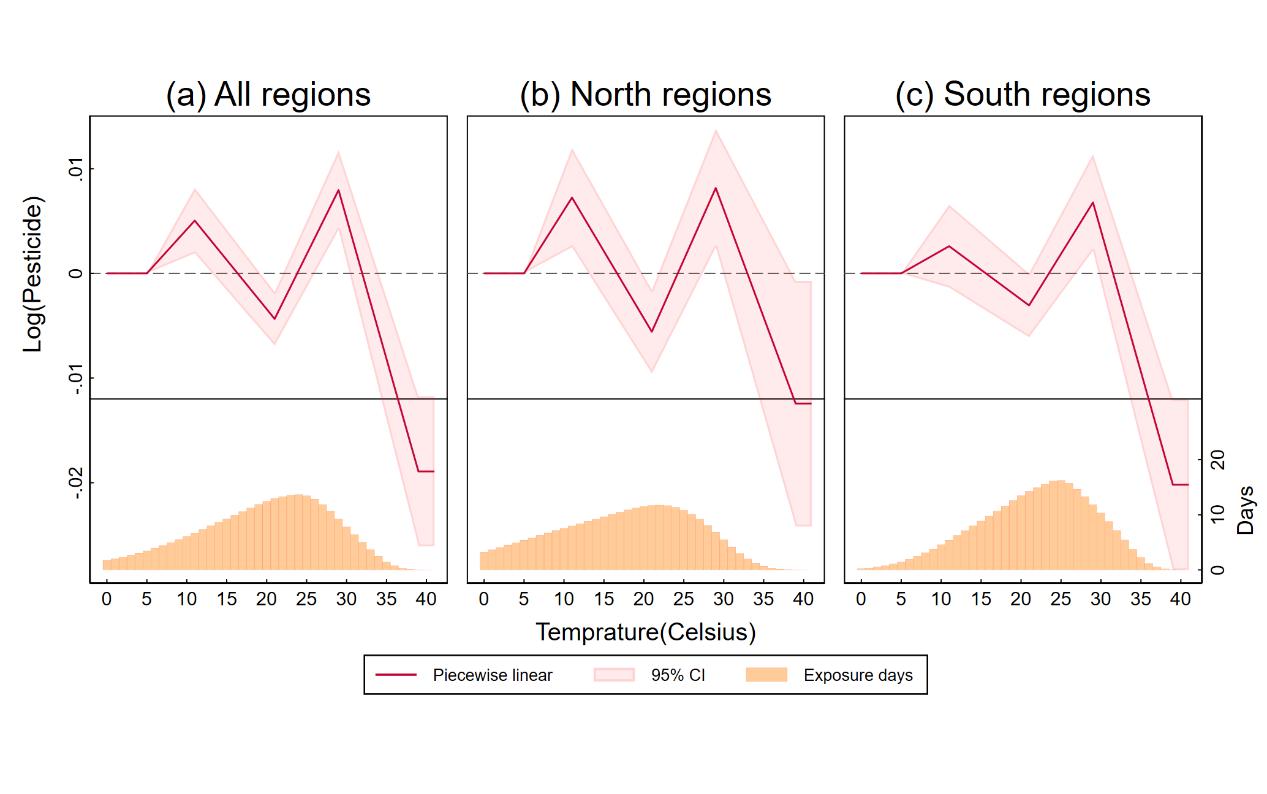
气候变化对农业生产的影响在很大程度上取决于农户的适应行为。本研究以农户的适应行为为切入点,聚焦气候变暖背景下农业化学品投入的调整,利用中国县级农业经济与气候面板数据和固定效应模型,考察生长期内农户如何根据天气变化调整农药施用,为农业生产应对气候变化提供新的实证证据。实证结果显示,农药使用量显著受天气影响,并呈现复杂的非线性温度响应。第一,在生长期内,随着温度升高,农药使用总量先上升后出现阶段性下降,随后再次上升,并在极端高温条件下再次下降。该响应在南方较北方更为明显,可能反映作物的农艺特性与区域差异。第二,鉴于作物层面的农药使用数据缺失,本研究创新提出一种基于最大熵的估计方法,在省级汇总数据基础上估算县级分作物的农药使用。第三,针对温度对农药使用总量的作用机制,本研究构建了一个经济学分解框架:将温度对农药总量的影响拆解为强度效应、结构效应和面积效应三种机制,结果表明短期内农药投入的调整主要通过强度效应(即单位面积农药使用强度)的调整来实现。第四,进一步的长期差分分析表明,温度对农药总使用量的影响随时间减弱,揭示农药投入对气候变化的响应集中于短期调整而非长期调整。总体而言,本研究的发现深化了对农业投入在气候变化下响应机制的理解,为制定气候适应与绿色农业转型政策提供了科学依据。
本研究是该团队在农业风险管理与安全发展领域的阶段性探索成果之一。本研究得到了国家自然科学基金-BMGF联合农业研究项目(72261147758)、国家社会科学基金(22VRC085)和浙江省哲学社会科学基金领军人才项目(24YJRC01ZD)的资助。
原文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/agec.70057